Cyphostemma Uter is a caudex-forming subshrub or shrub native to the arid regions of southwestern Angola and northwestern Namibia. It typically grows in desert or dry shrubland biomes, favoring well-drained, rocky or gritty soils with minimal water and plenty of sunlight. The plant belongs to the Vitaceae family and is known for its succulent characteristics and thickened stem base (caudex), which helps it store water in its dry habitat
It thrives in arid, rocky environments and can be cultivated as a bonsai or indoor plant under appropriate conditions, requiring very bright light or full sun and careful watering—rarely and sparingly during cold periods, and moderately during the growing season
. It is drought-resistant and adapted to hot, dry climates with minimum winter temperatures above 10°C (50°F)
There is a known variety called Cyphostemma uter var. macropus, which shares the same origin and growing conditions in southern Africa
In summary, Cyphostemma uter is a rare, drought-tolerant succulent shrub from southern Africa, valued for its caudex and suitability for bonsai or indoor cultivation in warm, sunny environments with well-drained soil
characteristics:
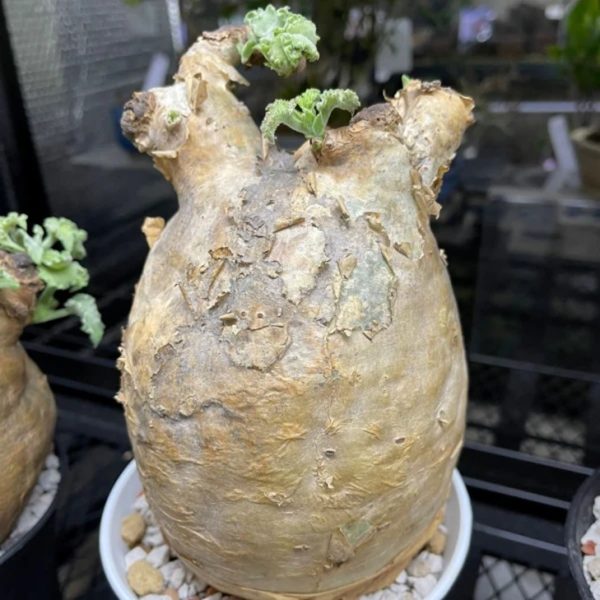
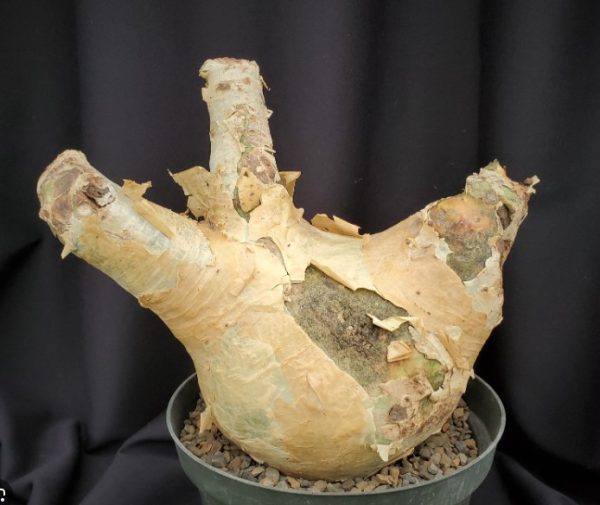
Habitat and Growth form: It is a deciduous, caudiciform succulent native to hot, dry, stony slopes in northwestern Namibia and Angola, typically found at altitudes of 100-450 meters. It grows as a low, much-branched shrub or small tree up to 1.5–2 meters tall with a stout, swollen caudex (water-storing trunk) that can be up to 60 cm in diameter, sometimes larger (Cyphostemma Uter)
Caudex and Bark: The caudex has dull white to orange bark that peels off in paper-like flakes, helping the plant manage heat and water storage. Branches are thick (7-30 cm diameter) with peeling bark, contributing to its distinctive sculptural form
Leaves :Leaves are alternate, fleshy, tough, and crowded at branch ends. They are green, triangular, 5-foliolate, about 8 cm across, hairy with undulate, serrated margins. The plant sheds leaves in severe drought to reduce water loss
Flowers and Fruits : It flowers in summer, producing greenish-yellow flowers arranged in cymes. The fruit are bright red, hairy berries, but the fruit’s epidermis contains crystals that can cause severe mouth irritation
Adaptation and arid Environment : The thick caudex stores water to survive prolonged droughts. The peeling bark reflects sunlight to keep the plant cool. It is drought-tolerant but grows actively in summer with some water. It is sensitive to overwatering, especially in winter dormancy, and requires well-drained, rocky or gritty soil
Cultivation Notes:Prefers full sun exposure and dry conditions in winter to prevent rot. It is slow-growing and considered difficult to cultivate, needing patience and careful watering. Mature plants can tolerate temperatures down to about -3°C (27°F) if kept dry and ventilated
These features collectively enable Cyphostemma uter to thrive in harsh, arid environments with intense sunlight, minimal water, and rocky substrates
Water storage mechanism
Cyphostemma Uter water storage mechanism, primarily its thickened caudex (swollen stem base), plays a crucial role in its survival during droughts by acting as a reservoir that stores water when it is available and slowly releases it during dry periods. This adaptation allows the plant to endure prolonged water scarcity typical of arid environments. The caudex’s succulent tissue can retain significant amounts of water, buffering the plant against dehydration and maintaining cellular functions even when soil moisture is extremely low.
Additionally, the plant’s peeling bark and tough, fleshy leaves reduce water loss by reflecting sunlight and minimizing transpiration. Leaf shedding during severe drought further conserves water. These structural and physiological features combined enable Cyphostemma uter to maximize water uptake during rare rains, store it efficiently in the caudex, and minimize water loss, thereby sustaining itself through extended dry spells typical of its native arid habitat (Cyphostemma Uter)
In general, such water storage strategies in succulent plants help maintain hydration, support metabolic activity during drought, and allow rapid recovery after rainfall, which is essential for survival in harsh desert conditions


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.